The digital world generates a staggering amount of data every day. This ever-growing flood is a significant challenge for organizations trying to process, store, and analyze it effectively.
Enter Hadoop, an open-source framework that has revolutionized big data management. Its ability to store and process vast data sets quickly and efficiently cemented its position as a cornerstone of data analytics and cloud computing.
This article explores the key aspects of Hadoop, including its core components and functionality, as well as its advantages, limitations, and real-world applications.
What Is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open-source framework designed to process massive datasets by leveraging the power of distributed computing. This paradigm involves spreading large datasets across clusters of computers instead of relying on a single powerful machine or a data warehouse.
The distributed approach allows Hadoop to handle massive volumes of data, scaling up to thousands of terabytes and beyond. Unlike traditional systems that struggle with such swathes of data, Hadoop's design and simple programming models make it cost-effective and reliable. Consequently, Hadoop has become synonymous with big data processing, offering a powerful solution for organizations that need to store, analyze, and extract insights from vast pools of information.
Hadoop Ecosystem
Hadoop is surrounded by a comprehensive suite of software solutions known as the Hadoop ecosystem.
This ecosystem contains various services and technologies that work with Hadoop to enhance data processing, storage, and analysis capabilities.
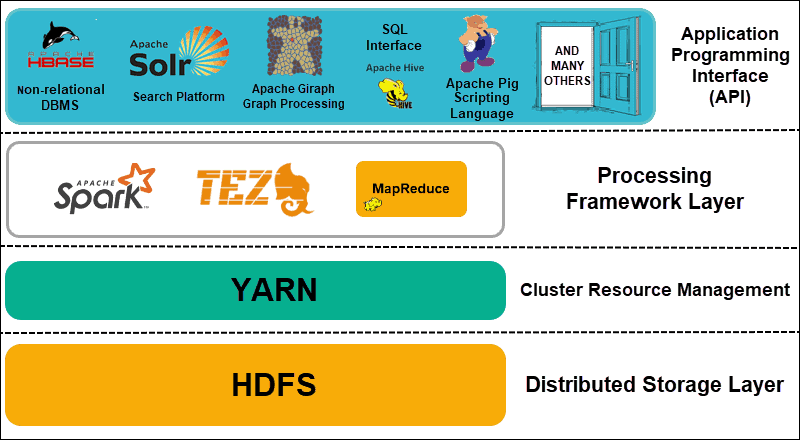
Components of Hadoop
The foundational elements of the Hadoop framework are known as its core components. These provide the essential functionalities that support the entire ecosystem and enable integration with additional tools and services both from the Apache Software Foundation and third-party developers.
Here are the three core components of the Hadoop ecosystem.
HDFS
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) tackles the challenge of storing massive datasets by distributing data across multiple machines.
Architecture and Storage Management
HDFS employs a master/slave architecture. The NameNode, acting as the central authority, manages the file system's namespace and regulates access. Meanwhile, DataNodes, distributed across machines, handle the storage of data blocks. This division of labor allows for efficient data storage and retrieval.
Data Replication and Fault Tolerance
Data loss is a concern in any distributed system. To address this issue, HDFS replicates each data block across multiple DataNodes, typically three times. This redundancy ensures that even if a node fails, the data remains accessible from other replicas. The design of HDFS prioritizes fault tolerance, guaranteeing continuous operation and data loss protection.
MapReduce
MapReduce tackles the challenge of efficiently processing vast datasets by leveraging a distributed approach on a Hadoop cluster. This programming model breaks down the workload into manageable pieces, enabling parallel processing through distinct Map and Reduce phases.
Map and Reduce Phases
In the Map phase, the data from HDFS is read and converted into a set of key-value pairs. The key-value pairs are then processed and sorted. The Reduce phase aggregates these key-value pairs into a smaller set of results, typically by summing, counting, or applying another operation to group data by key.
This two-step procedure enables efficient processing of large datasets by distributing the workload across multiple nodes.
Shuffling and Intermediate Data Management
The shuffle phase is critical for redistributing data so that all key-value pairs with the same key are brought together on the same reducer. This process ensures that the Reduce phase has all the relevant data necessary for aggregation. Intermediate data management, part of the shuffle process, handles the sorting and transfer of data between the Map and Reduce phases, optimizing data flow and processing efficiency.
YARN
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) manages resources and schedules jobs in the Hadoop ecosystem, enabling more efficient cluster utilization and application management.
Job Scheduling and Resource Allocation
YARN's architecture contains a global ResourceManager that oversees the allocation of system resources across all applications in the cluster. ApplicationMasters, specific to each application, manage the execution of tasks within the application. This separation of concerns allows YARN to optimize resource utilization by dynamically allocating resources based on need, significantly improving the efficiency of job scheduling and execution.
Containerization and Execution
YARN employs containers to manage task execution, encapsulating tasks in a controlled environment. Containerization allows for efficient resource management and standardized task execution across different nodes, improving resource utilization and operational efficiency.
Hadoop Tools
Beyond its core components, the Hadoop ecosystem includes various tools and services that extend and complement its data processing capabilities.
HBase
HBase is a column-oriented NoSQL database designed to run on top of the HDFS. It is optimized for quick read-and-write access to large datasets, making it suitable for applications that require real-time data access, such as web analytics.
HBase's architecture allows it to scale horizontally, adding more nodes to accommodate growing data without downtime.
Apache Hive
Apache Hive provides a SQL-like interface (HiveQL) to query data stored in HDFS and other compatible file systems like Amazon S3. It translates these queries into MapReduce, Tez, or Spark jobs, making it easier for users familiar with SQL to interact with data in Hadoop.
Hive is particularly useful for data warehousing tasks because it manages and queries structured data across distributed storage.
Apache Pig
Apache Pig is a high-level platform for creating MapReduce programs used with Hadoop. Its language, Pig Latin, simplifies the complexity of writing MapReduce algorithms, allowing for complex data transformation and analysis with simple scripts.
Pig also supports user-defined functions (UDFs) for handling tasks like data filtering, sorting, and aggregation, making it flexible for various data processing needs.
Apache Spark
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It can run standalone, on Hadoop, or in the cloud, processing data up to 100 times faster than traditional MapReduce tasks by leveraging in-memory computing and optimizing query execution.
Spark supports multiple languages (Scala, Java, Python, and R), allowing developers to write applications in their preferred language. It's equipped with libraries for SQL (Spark SQL), machine learning (MLlib), graph processing (GraphX), and data streaming (Structured Streaming), making it a versatile tool for a range of data processing and analytics tasks.
Consider reading our article Hadoop vs. Spark to learn the key differences between them and when you should choose one or the other, or both.
Apache Flume
Apache Flume is a distributed service for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and moving log data to the HDFS. It is designed to handle high-throughput data streams and has a simple and flexible architecture based on streaming data flows.
Flume's use of configurable agents that can be distributed across multiple sources makes it ideal for streaming data into Hadoop for further analysis.
Apache Sqoop
Apache Sqoop (SQL-to-Hadoop) is a tool that efficiently transfers bulk data between Apache Hadoop and structured data stores such as relational databases. Sqoop automates most of the process, using database schemas to define the import and export process.
It also supports incremental loads for regularly updated databases, making it a critical tool for integrating Hadoop with existing data infrastructures.
Apache Oozie
Apache Oozie is a workflow scheduler system that manages Hadoop jobs. Workflows in Oozie are defined as a collection of actions (Hadoop MapReduce tasks, HDFS operations, etc.) arranged in a directed acyclic graph.
Oozie enables users to schedule jobs, link them together in complex workflows, and manage dependencies, simplifying the automation of repeated tasks.
phoenixNAP's Bare Metal Cloud offers dedicated physical servers combined with the flexibility and scalability of the cloud. This solution provides the high-performance computing power and storage capacity necessary for running Hadoop clusters effectively.
Unlike virtualized environments, bare metal servers provide dedicated resources, ensuring consistent performance for data-intensive Hadoop tasks without virtualization overhead.
How Does Hadoop Work?
Hadoop operates by breaking down big data tasks into smaller fragments, which are then distributed across a Hadoop cluster. Each node in the cluster processes the data stored on it, eliminating the need to transfer data across the network.
The two main components, HDFS and MapReduce, work together as follows: HDFS distributes the data, and MapReduce processes it. YARN, another core component, manages resources in the cluster, scheduling jobs and tasks.
Processing Workflow
The Hadoop processing workflow is a structured approach to managing data through three key stages.
- Data ingestion. The initial stage involves loading data into HDFS.
- Processing. This stage involves analyzing data using MapReduce jobs.
- Output. Once processed, the resulting data is stored back into HDFS or transferred to another designated storage system, allowing for further analysis or utilization.
Distributed Processing Concepts
Hadoop uses distributed processing techniques to enhance performance and data reliability.
- Parallelization. This concept involves dividing tasks into smaller sub-tasks processed concurrently across different nodes to improve speed and efficiency.
- Fault Tolerance. Using data replication allows the system to continue operating smoothly even if some nodes fail.
Navigating the intricacies of Hadoop's architecture and available tools can be challenging for first-time users.
If you are overwhelmed, our comprehensive article on Hadoop architecture provides clear explanations and helpful diagrams that will simplify learning the Hadoop ecosystem.
Advantages of Hadoop
For organizations needing to process and analyze data, Hadoop offers several compelling advantages.
- Scalability. Hadoop's distributed computing model allows it to scale efficiently from a single server to thousands of machines. Each node in a Hadoop cluster offers local computation and storage, facilitating the efficient processing of large datasets.
- Cost-effectiveness. By leveraging commodity hardware for storage and processing, Hadoop enables organizations of all sizes to manage massive datasets.
- Flexibility. Hadoop can process all types of data from various sources, whether structured, unstructured, or semi-structured. This flexibility allows organizations to use Hadoop for a range of purposes, from analytics to data warehousing.
- Fault Tolerance. Hadoop ensures data integrity by replicating data blocks across multiple nodes. If a node fails, Hadoop will automatically redirect tasks to another node, minimizing downtime and data loss.
- High Efficiency. Through parallel processing, Hadoop significantly speeds up data analysis. It divides tasks across numerous nodes, processing large datasets faster than traditional systems.
Drawbacks of Hadoop
Despite its advantages, Hadoop has drawbacks you must consider.
- Complexity. Setting up, configuring, and optimizing a Hadoop environment requires a deep understanding of its underlying principles and components. This complexity is a barrier to entry for organizations that lack in-house expertise.
- Latency. Hadoop is optimized for batch processing large volumes of data. You will experience higher latency in data processing tasks compared to systems designed for real-time analysis.
- Security. Early versions of Hadoop had limited security features. Although subsequent updates have improved security, ensuring data integrity in a distributed system is a complicated task that requires careful planning and implementation.
- Data Privacy. Distributed data storage and processing across multiple nodes increases the risk of unauthorized access. Protecting sensitive information requires comprehensive security measures and access controls to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with data protection regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI.
Use Cases for Hadoop
Hadoop is used across a range of industries for various applications.
- Big Data Analytics. Organizations use Hadoop to process and analyze large datasets to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform business strategies and decisions.
- Data Warehousing. Hadoop serves as a repository for massive volumes of structured and unstructured data. It can facilitate complex queries and analyses over large datasets.
- Log Processing. Many organizations leverage Hadoop to process and analyze log data generated by websites and applications, helping to improve services and troubleshoot issues.
- Recommendation Systems. By analyzing user behavior and preferences, Hadoop can power recommendation engines that suggest products, content, and services to users.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention. In the finance and retail sectors, Hadoop analyzes transaction data to detect and prevent fraud.
- Data Archiving. Hadoop provides a cost-effective solution for archiving data and ensuring it remains accessible for future analysis and compliance.
Unleashing the Power of Big Data
As a foundational technology for big data analytics, Hadoop provides a reliable framework for efficiently storing, processing, and analyzing data across distributed computing environments. It is an indispensable tool for companies that manage vast amounts of information. Furthermore, Hadoop levels the playing field by empowering organizations of all sizes to harness the power of big data, eliminating the significant computing resources that once posed a barrier to entry.
As the volume, variety, and velocity of data creation and consumption expands, Hadoop's role in data management is set to grow. Instead of being overwhelmed by your data, use Hadoop to unlock valuable insights and make informed decisions that propel your business forward.



