As technology rapidly advances, there are numerous options available to businesses for running applications and software on the cloud. Several factors need to be considered when deciding if cloud infrastructure is the right choice. We’ll go through the main pros and cons of Cloud-based ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning software system) to help you navigate through the options.
We know it’s not easy to migrate into the cloud environment, and many companies continue to rely on trusted legacy software and on-premise applications to do business. Yet, Cloud-based ERPs offer many advantages such as lower up-front costs, hands-off maintenance, and automatic updates, making it worthy of serious consideration.
Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud computing continues to grow in popularity since it offers companies scalability, agility, and the ability to save resources and money. The wide range of choices forces decision-makers to answer critical questions about their goals. It’s especially true for a company going through a significant digital transformation, such as implementing a new Enterprise Resource Planning software solution.
In such a highly competitive technological landscape, using an ERP system is the best way to tackle the competition. It allows an enterprise to integrate various functions into one system and streamlines information and processes across the entire organization. The decision is whether to keep these processes on-premise or to shift them to the cloud using SaaS (Software as a Service).
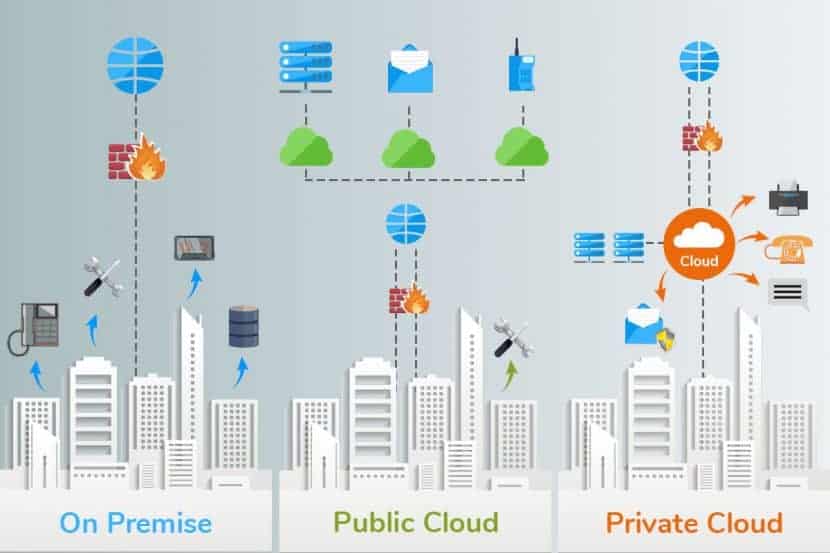
To help you understand Cloud-based ERP software better, we’ll first look at On-premise ERP systems and examine the two concepts, including their pros and cons.
How Cloud ERP Works
Cloud-based ERP solutions involve organizations paying a subscription fee to providers to use the software. The software is usually accessed online through a server owned by the software provider. Under cloud solutions, the software vendor is responsible for the server infrastructure data integrity, updates, backups, and security measures.
A company’s applications are hosted offsite when using a cloud-based server, involving no capital expenses. Companies can back up their data regularly and are only required to pay for the resources it consumes. Cloud ERP solutions are ideal for those organizations that are aiming at global expansion, harnessing the reachability of cloud technology to connect with customers and partners almost everywhere, quickly.
Benefits of Cloud ERP
- Software functionality: Working in cloud-based environments makes it easy to create and build towards establishing a high degree of integrated functionality, or to add more users to the system quickly. This setup allows businesses to scale faster, especially if an organization plans on expanding overseas.
- Technical Deployment: Deployment is much simpler, faster, and less expensive, as no on-site infrastructure is required.
- Costs involved: Organizations using the Software-as-a-Service model of cloud technology is a more cost-effective option for vendors and organizations alike. Many businesses also prefer monthly payments for their software usage for budgeting reasons, which also saves significantly on IT management and support overheads.
Private or Public cloud?
The two options here go with either Public or Private cloud enviroments. With the private cloud, a company is responsible for the maintenance, management, and updating of hosted data centers as all data resides on the company’s intranet. Over time, servers need upgrading or replacing, which can become very expensive. The private cloud offers a high level of security since data is accessed only via secure and private network links. Bigger enterprises with sensitive data are more likely to choose this cloud option.
The greater advantages come with public cloud-hosting. The primary benefit is that you are not responsible for any management of the hosting solution. Only the provider is responsible for the upkeep of their data centers. Smaller enterprises prefer this option as it reduces lead times for testing, which allows for quick deployment of new products. Security issues and disaster recovery would be the only concern with using a public cloud that can be remedied with built-in redundancies. The right provider will have a plan for protecting your assets in the event of an attack or natural disaster.
On-Premise ERP: Defined
On-premise software or premise applications refers to the traditional way in which organizations acquire and use software programs. It generally requires the organization to pay a significant amount, typically the total cost, upfront. In exchange, they receive a product with full licensing, capable of being used on the company’s server. Organizations are thus required to manage and maintain their physical computer servers internally, primarily when backups and upgrades are being performed.
Businesses which generally operate in highly regulated industries, or those working with critical and confidential data, give high priority to data security. It’s the reason why many organizations have opted for on-premise ERP solutions; they want to keep their sensitive data secure within in-house servers.
Features
- Software Functionality: On-premise ERP providers themselves, usually apply all relevant patches and updates, when required. This setup makes this software solution less scalable as businesses are required to invest in more resources if they want to expand critical areas, such as bandwidth.
- Technical Deployment: Software licenses are typically installed within the organization’s server. Such installations, therefore, are not limited by slow or unreliable network connections. However, server maintenance requires some technical knowhow, which is best left to professionals and require additional hiring or investment.
- Costs involved: On-premise ERP solutions are more expensive to acquire and implement. The management is also responsible for covering any ongoing expenses related to information security management, maintenance of the hardware and software, and replacing servers. However, no continuous subscription fees are involved.
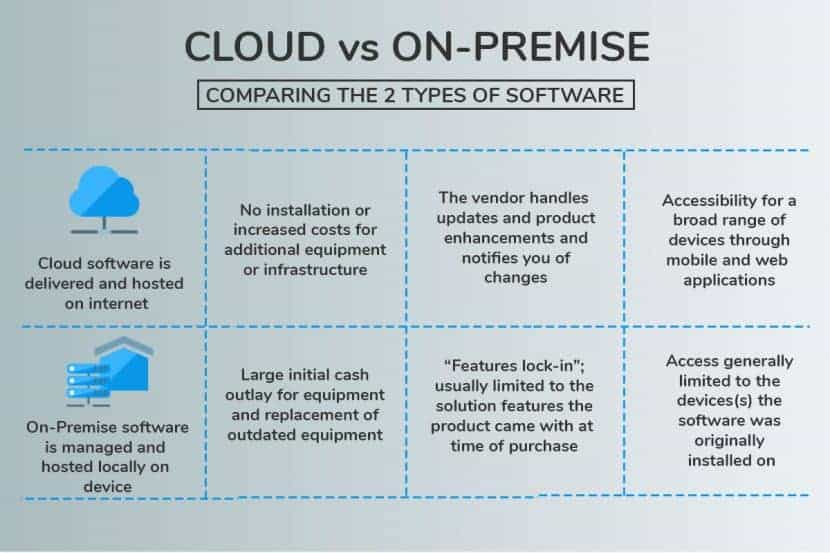
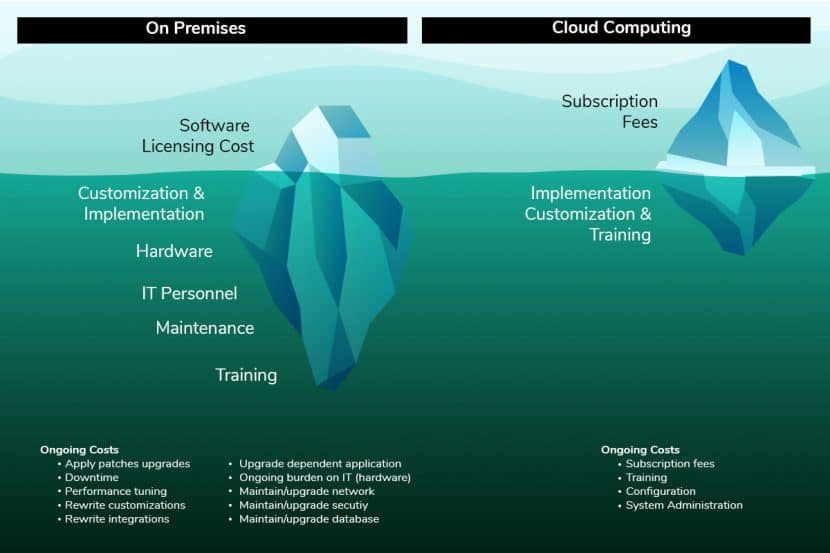
How to Choose the Right Enterprise Resource Planning System Option?
When organizations choose between the two options, they examine at the bottom-line first and deem it as the deciding factor in determining which technology will suit them best. Cost should not be the only deciding factor. Others need to be taken into consideration.
Aspects we recommend an organization should evaluate include:
- Bandwidth: The capabilities of the organization’s internet connectivity and infrastructure.
- Future Growth: The scalability requirements of the organization, including evolving business models, strategic business plans, or plans for expansion.
- Staff: The costs related to internal IT skills and HR resources.
- Budget: The organization’s allocated budget and other financial considerations, such as the best payment option or tax considerations.
- Resource Utilization: Cloud-based ERP solutions are more appealing to organizations because it uses fewer resources and provides more flexibility when it comes to accessing functionality and data.
- Complex Implementation: Cloud-based software can have multiple tenants or a single-tenant, depending on the cloud model chosen. This setup allows for the complex implementation of systems that have stringent security needs and sensitive data.
- Control over Data: For organizations that value control over data more than cost-effectiveness, on-premise solutions are ideal for them. On-premise solutions are also more effective for organizations working with unreliable or unstable internet connections.
Check out our in-depth guide on cloud computing cots.
Cloud ERP Solutions Compared
For businesses to make well-informed decisions about which system to implement, the following comparisons give a clearer idea of the two options available.
| Comparison of Features | On-Premise ERP | Cloud-based ERP |
| Level of Control | Enterprises retain the rights to all of their data and are in full control of what it does with it. Organizations in highly regulated industries thus prefer on-premise solutions to cloud-based alternatives | Data and encryption keys are managed and stored by the third-party software provider and not with the company. This setup can pose a problem for accessing data during periods of unexpected downtime. |
| Compliance | Companies using on-premise solutions often fall under strict regulatory control. The nature of the data they work with contains delicate or critical information that requires full compliance with the laws in place. Thus on-premise solutions are a safer option. | Enterprises working with cloud computing solutions are required to conduct due diligence. They must ensure that the software provider is compliant with the required regulatory mandates in the industry and country they are operating in. |
| Data Security | For organizations such as government entities or national banks, keeping their data on-premise is preferred for accountability reasons and thus choose on-premise solutions. | Security in the cloud environment is one aspect that has been a hurdle in recent years. The risk of suffering data breaches and loss of data such as intellectual property can deter any organization from choosing cloud-based solutions. |
| Deployment | Resources are deployed on-site and in-house, which falls within an organization’s own IT infrastructure. | Resources are hosted on the service provider’s premises when using any sort of cloud computing model. |
| Customization | Generally, more customizable but time-consuming as well. Additionally, there is no guarantee that the customizations will function as intended when the vendor updates the software. | Cloud-based ERP solutions offer greater stability as the vendor itself handles all customizations. |
| Implementation | The organization has a higher degree of control when implementing the system. On the other hand, it is a time-consuming process. | Organizations have significantly less control over the implementation process. It is less time-consuming. |
Cloud ERP Security
Despite the general misconception about Cloud ERP solutions lacking security, modern vendors have increasingly focused on delivering a product with top-notch security held to international standards. However, proper implementation of these security standards requires a high quality IT management, which companies need to take into account.
Each year, more companies have started migrating their data, systems, and services over to the cloud due to the various limitations of on-premise ERP. Migration to a hosted server can provide immense benefits such as quick addition of storage systems, overall improvement of the team, and built-in security systems. The chances of downtime are reduced significantly, enabling organizations to maximize available resources.
Many companies are also using hybrid solutions such as on-premise clouds to avoid any third-party control. This allows you to run apps and services, while having workloads placed in the cloud or on-prem data centers, as appropriate.
The cost optimization that the cloud offers remains one of the most attractive features for organizations that have started expanding. On-premise solutions, alternatively, appear to give more control to organizations, and for some industries, this is worth the higher cost. Yet, more control does not mitigate the risks of suffering cyber attacks and instead increases the organization’s accountability.
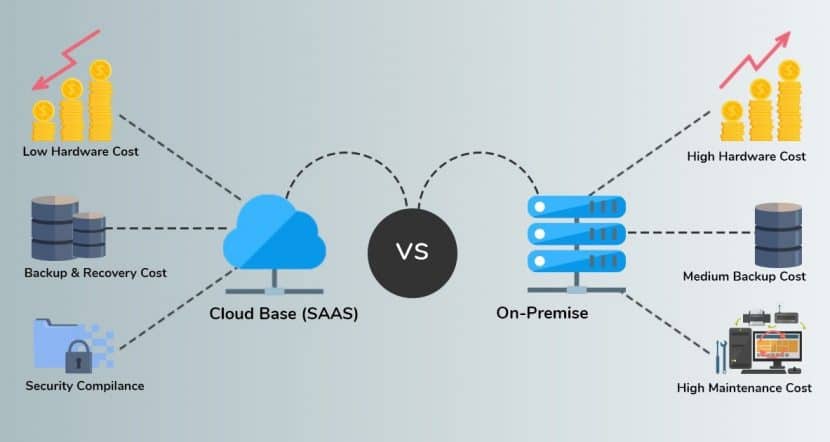
The Bottom Line on ERP Systems
The final decision rests with the organization’s management and how they see their future. Do they want to remain contained and in control, or do they want to take advantage of cloud computing power and cloud-based solutions?
For larger enterprises, they can invest significant capital in on-premise ERP solutions but it isn’t for everyone. For medium to small scale businesses that have limitations on their budget, cloud ERP software alternatives are the only answer. They simply save time and money.
Whichever the case, every successful business requires a healthy and dynamic data ecosystem. Having a reliable and scalable infrastructure in place which can support end-to-end visibility of data flows, fast and secure file transfers, data transformation, and storage is integral to success.
To take a step toward the cloud, and learn more on how cloud software systems can run your business, contact us today.



