Introduction
SSH (Secure Shell) is a cryptographic network protocol that allows secure communication between two computers over an unsecured network.
SSH provides a secure way to access a Debian system remotely over a network. It encrypts the communication between the client and the server, protecting sensitive information such as passwords and data transferred over the network.
The following text will show you how to enable SSH on Debian 12.

Prerequisites
- An SSH server and a client (this tutorial uses Debian 12 for the server).
- sudo privileges for each system.
- Access to the terminal.
How to Enable SSH on Debian
A secure connection is important when connecting remotely. Otherwise, the machine's security is compromised. The following five steps explain how to enable SSH and establish a secure connection on Debian.
Step 1: Update the Package Manager
Before installing new software, update the software repository list on both machines with the following command:
sudo apt update
The output for the server machines shows the update process. The same process happens on the client's computer.
Step 2: Install SSH Server
On the system that acts as a server, run the following command:
sudo apt install openssh-server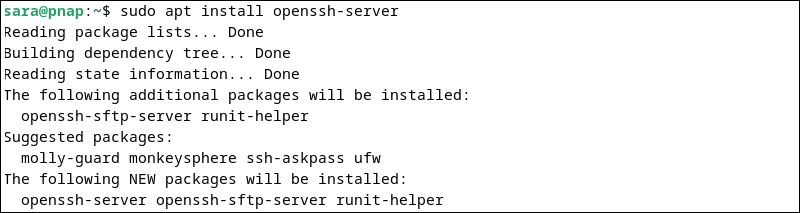
Once the installation completes, check the SSH service status with the following command:
sudo systemctl status ssh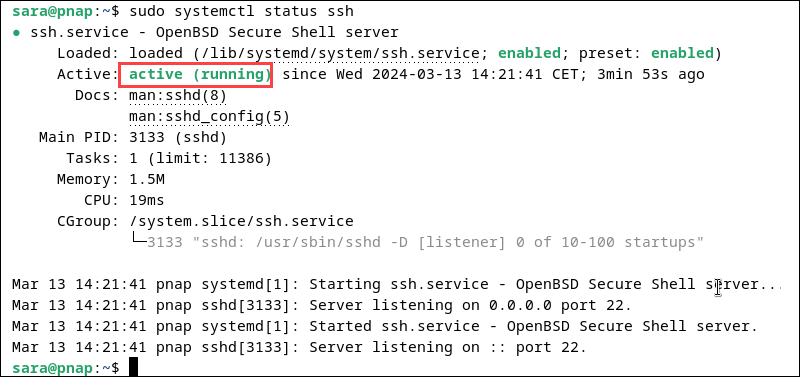
The system confirms the SSH service is running.
Step 3: Start and Stop the SSH Server
In case the SSH status is not active, start the service with:
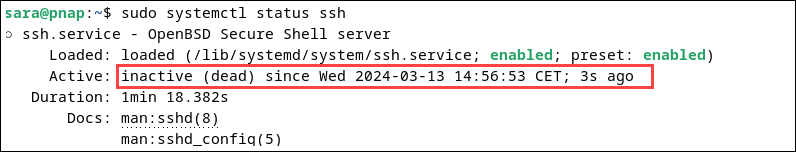
sudo service ssh startThe command has no output. To stop the SSH host server, enter the following:
sudo service ssh stopThe command shows no output. However, if you check the service status, the system indicates the SSH is inactive and shows the exact date and time it stopped.
The service will be stopped only until the next reboot. To turn off SSH indefinitely, enter:
sudo systemctl disable ssh
To enable the SSH service again, run:
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Step 4: Get Your Server IP Address
When configuring a server locally, use the terminal to find your IP address with the ip command:
ip a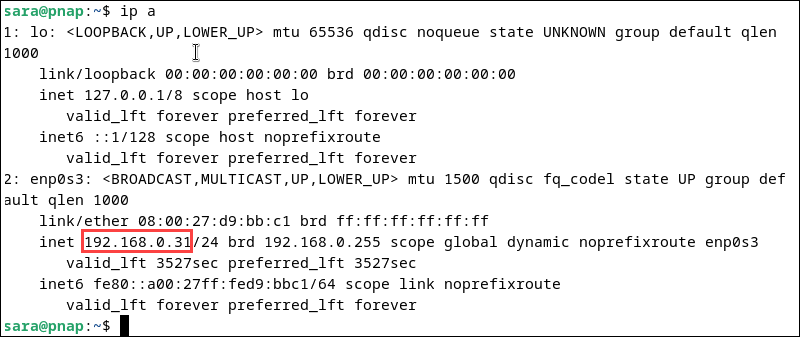
The 192.168.0.31 private IP address is associated with the network interface enp0s3. This interface is typically used for communication with other devices on the network.
Note: If you're connecting from outside the local network, determine the public IP address of the machine you want to connect to. To find it, use curl ifconfig.me.
Step 5: Install SSH Client Service
By default, most Linux systems have the SSH client installed. If yours doesn't, enter the following command in the client machine terminal:
sudo apt install openssh-client

How to Connect to a Server Using SSH
Once both the client and the server machine are set up, connect to the server from the client machine using SSH via the following command:
ssh UserName@IPAddressOrHostnameThe command consists of:
ssh. The primary command-line tool for SSH connections.UserName. The username used to log in to the remote machine. Replace with the authorized user username on the server machine. In this example, it'ssara.IPAddressOrHostname. The IP address, domain, or hostname of the remote machine you want to connect to. This example uses the IP address192.168.0.31.
Therefore, in this example, the command is:
ssh [email protected]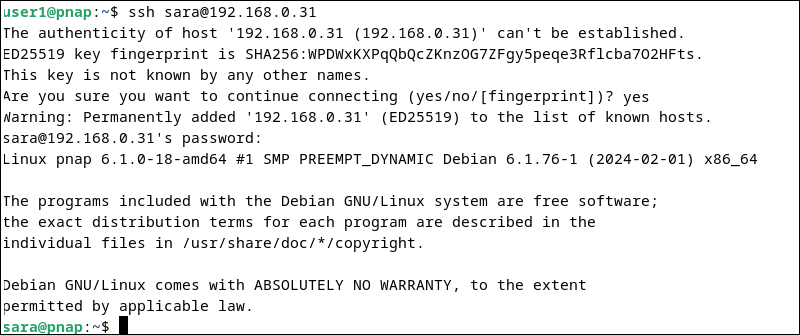
The remote system prompts for a password. Once completed, the terminal changes to username@hostname (in this case, sara@pnap), indicating the commands you run are being executed on the remote server.
How to Configure Firewall for SSH
Configuring the firewall for SSH is an essential step when enabling SSH because it ensures SSH traffic is allowed through the firewall. In some cases, firewalls block incoming connections to the system as a security measure. Therefore, to allow SSH connections from other machines, configure the firewall to permit SSH traffic.
To allow SSH access, use the command:
sudo ufw allow ssh
When you run this command on the server machine, it adds a rule to the UFW firewall configuration that permits incoming SSH traffic on the default SSH port (TCP port 22). This allows clients to connect to the SSH server running on the server machine.
Port Forwarding
To enhance security when accessing an SSH server from outside your local network, configure port forwarding using the firewall or router settings. Port forwarding lets external traffic access services on the private network by directing incoming traffic from a router's specific port to a corresponding port on a local machine.
For detailed instructions, refer to the firewall or router documentation.
Note: By default, SSH uses port 22 for communication. You can configure a firewall or router to accept SSH traffic on a different port. This is a helpful solution when opening up your server to the internet traffic. Changing the port restricts access to only those who know the correct port, thereby limiting unauthorized connections.
Conclusion
By following the steps outlined in this article, you have successfully enabled an SSH connection on Debian. You can now connect to a remote host securely and continue to manage your servers in a safe environment.
Next, learn about ten SSH commands in Linux.