Introduction
Reinstalling an operating system and starting fresh is helpful if an upgrade fails or there is an issue with drivers. Other situations that might require an OS reinstall are a faulty GRUB loader or issues whose cause is difficult to pinpoint.
Although many issues have specific solutions, sometimes reinstalling the OS and starting fresh is the fastest way to eliminate the problem.
This tutorial will show how to reinstall Ubuntu in a few steps.

Prerequisites
- A USB drive (at least 4 GB).
- Internet connection.
Ubuntu Reinstallation Guide
Follow the steps below to reinstall Ubuntu on your machine. Backing up is the first step before starting a system reinstallation.
Step 1: Backup
Reinstalling Ubuntu should not damage or erase personal files. However, make sure to backup your data. Use an external drive or USB and copy any important files you don't want to lose.
After the reinstallation, the following should be preserved:
- The /home directory with your files and settings.
- The entries in the boot menu (in case of multiple OSes).
Note: Make sure to backup applications installed in the system directory. For example, LAMP installs in the system directory and will be erased during reinstall.
Step 2: Download Ubuntu
Browse to the official Ubuntu downloads page. Choose the Ubuntu version you want to reinstall and click the Download button.
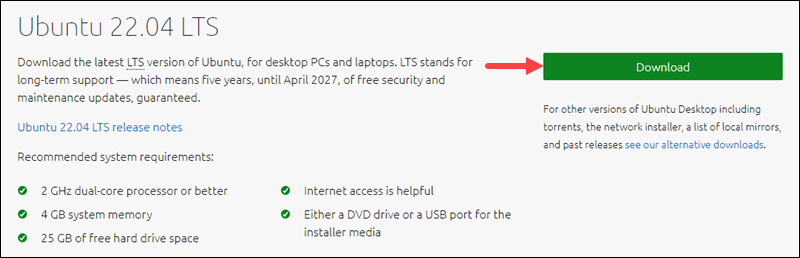
Wait for the ISO image to finish downloading.
Note: See how to fix broken packages in Ubuntu and fix problems without reinstalling the system.
Step 3: Create Live USB
To create a live USB for reinstalling Ubuntu, make sure to have:
- A 4GB or larger capacity USB stick/flash drive.
- The Ubuntu ISO file downloaded in the previous step.
Important: All data on the USB device will be erased.
Create Live USB in Ubuntu
If you still have access to your Ubuntu system, create a live disk using the Startup Disk Creator tool available by default.
Follow the steps below to create a bootable USB on Ubuntu:
1. Insert a USB stick into an available USB port.
2. Click the Show Applications button to open the app drawer.
3. Type "startup disk creator" in the search field and select Startup Disk Creator.

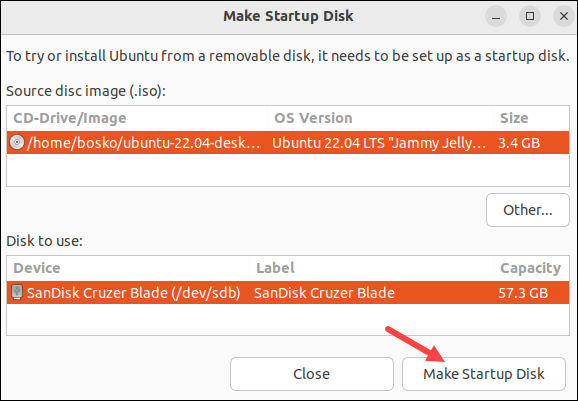
4. In the tool, select the target USB drive in the Disk to use section. Click the Other... button to load the ISO image in the Source disc image (.iso) section.
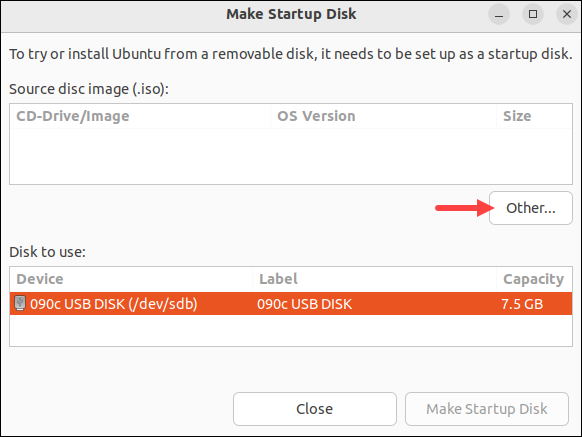
5. Select Make Startup Disk button and to create the Live USB.
7. Click Yes to continue when prompted.
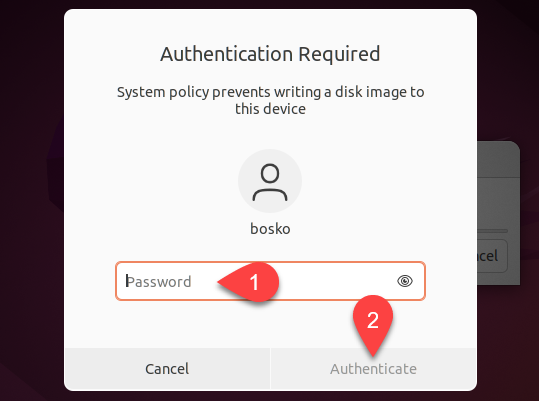
8. Enter the administrator password and click Authenticate to continue writing to the device.
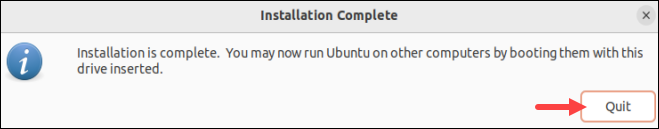
9. When the tool finishes writing the image to USB, an info message appears stating that the installation is complete. Click Quit to close the dialog box and proceed to follow the steps for reinstalling Ubuntu.
Note: If you are using Windows, but don't want to dual boot with Linux, see how to run Ubuntu on Windows as a VM with Hyper-V.
Create Live USB in Windows
Use Rufus or any other third-party tool to create a bootable USB drive on Windows. For Rufus, follow the steps below:
1. Insert your USB stick into an available USB port.
2. Navigate to the official Rufus website and scroll down to the Downloads section. Click the link to download the latest Rufus version.

2. Run the downloaded file. During the first launch, Rufus prompts to regularly check for online updates. Select the preferred option. Rufus automatically recognizes the USB drive.
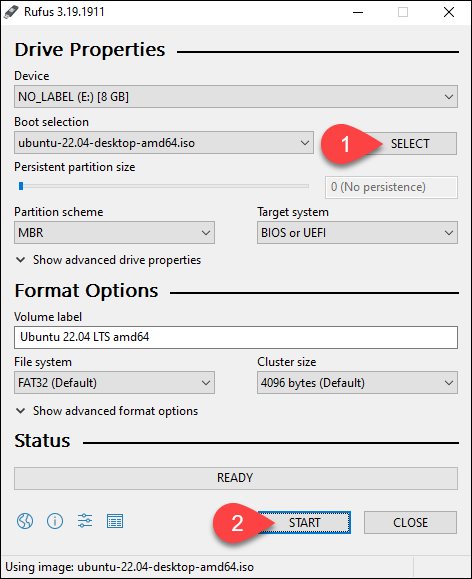
4. Click the SELECT button and locate the downloaded Ubuntu ISO image.
5. Click START to format the USB drive and start writing the image to the device.
Step 4: Reinstall Ubuntu
Do not remove the USB drive and restart the machine. On the post screen, depending on your machine brand, press the F2/F10/F12 key to enter the BIOS settings. In BIOS, ensure that Removable Devices/USB is at the top of the Boot order list. Save the changes and exit BIOS.
The system restarts and boots from the live USB. Follow the steps below to reinstall Ubuntu:
1. In the GNU Grub menu, select the Try or Install Ubuntu option and press Enter.
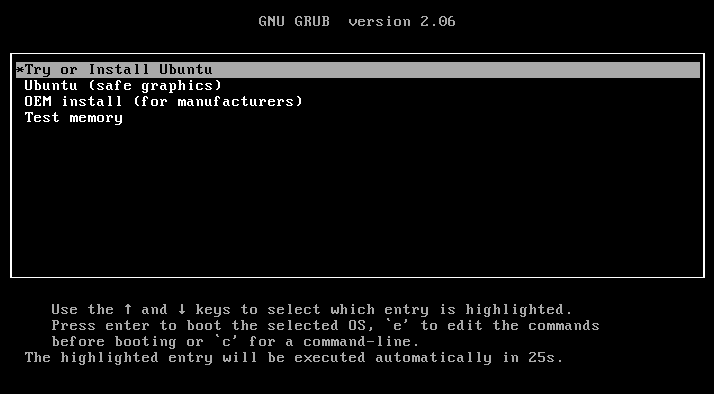
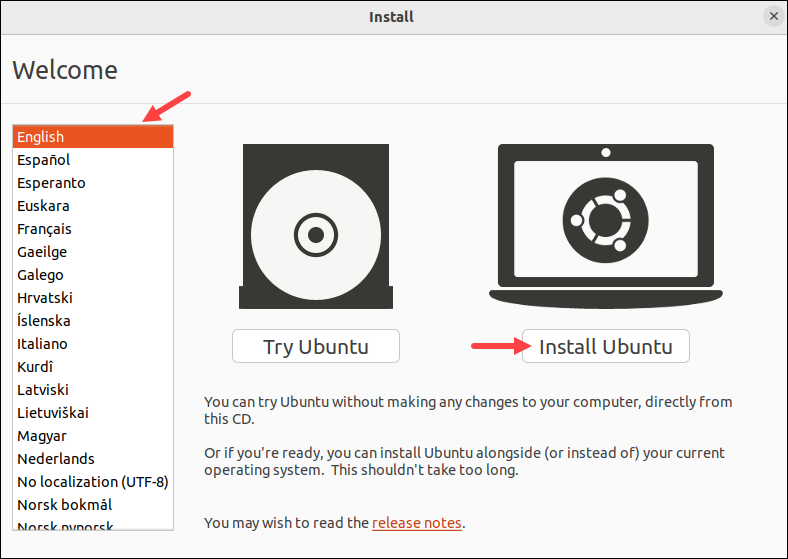
2. On the Welcome screen, choose your preferred language and select the Install Ubuntu option.
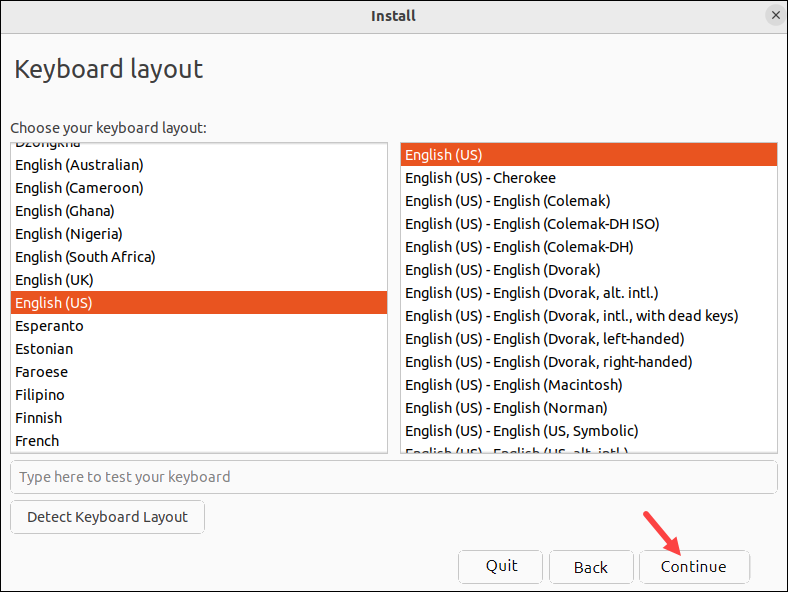
3. Select the keyboard layout and click Continue.
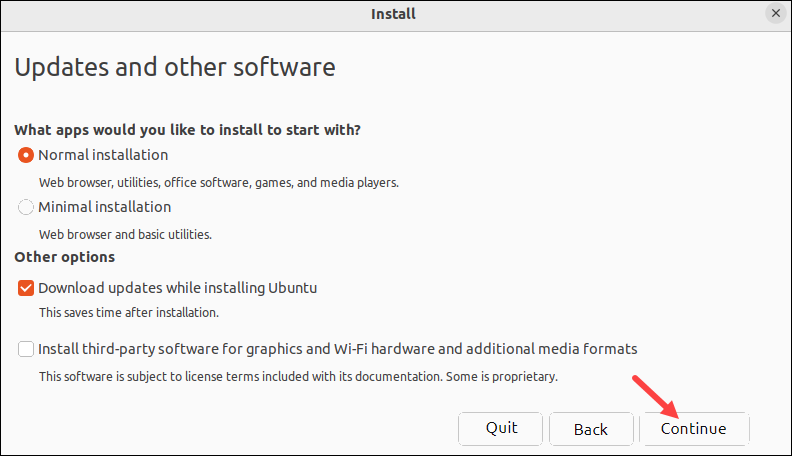
4. Choose the Normal or Minimal installation type depending on which apps you want to install. Optionally, check the boxes in the Other options section to download updates while installing and install third-party software for the graphics and Wi-Fi devices. Click Continue.
5. On the Installation type screen, select the Reinstall Ubuntu option to reinstall Ubuntu and keep personal files intact. Alternatively, choose the Erase Ubuntu and reinstall option to format the hard drive and install a fresh Ubuntu instance on the machine. Click the Install Now button to start the installation.
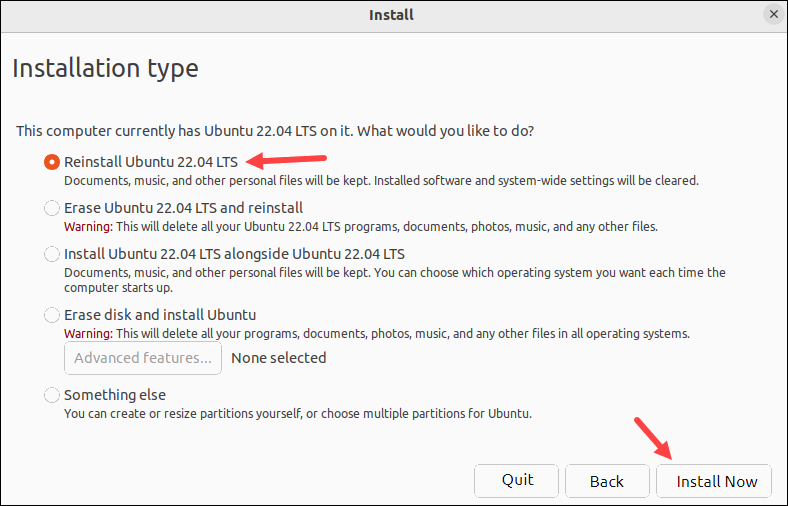
Important: If you are running a Windows and Ubuntu dual boot, select the Something else option and reinstall Ubuntu from there. Otherwise, the Windows partition gets formatted, too.
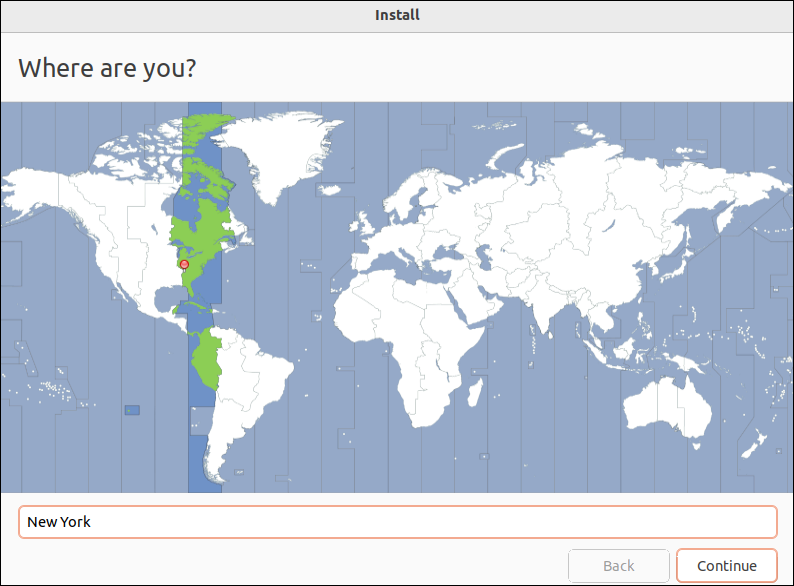
6. Choose your time zone and click Continue.
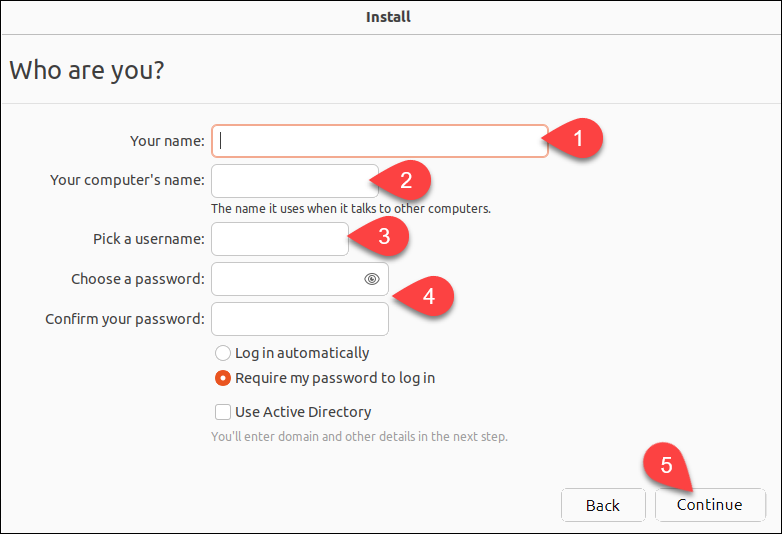
7. Create a username and password and click Continue.
8. Wait for the installation to finish. Then, remove the USB drive and boot into the system.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed how to reinstall Ubuntu while keeping all personal files or starting fresh. If you are on an older Ubuntu version and want to try the new 22.04 LTS version, follow our tutorial to install Ubuntu 22.04, or see how to upgrade to Ubuntu 20.04.